Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 /MOX fuel oxidation under severe light water reactor accident conditions
/MOX fuel oxidation under severe light water reactor accident conditionsLiu, J.; Miwa, Shuhei; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 37, p.101532_1 - 101532_5, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Takano, Masahide; Kumagai, Yuta; Sato, Soichi; Tanaka, Kosuke
Current Location of Fuel Debris Chemistry, 178 Pages, 2023/11
Considerable efforts have been devoted to the decommissioning of the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) and now the retrieval of fuel debris is being proceeded on a trial basis. It can be said that the succession of science and technology related to debris, that is, human resource development, is important and indispensable. For that reason, we thought that a specific textbook on decommissioning is necessary. Regarding the 1F fuel debris, we still do not know enough, and it would be difficult to describe the details. However, 12 years have passed since the accident, and we have come to understand the situation of 1F to a certain extent. At this stage, it is essential for future development to organize the current situation by combining examples of past severe accidents. Therefore, we presented in this book the current state of fuel debris chemistry research from the perspectives of solid chemistry, solution chemistry, analytical chemistry, radiochemistry, and radiation chemistry.
Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Morishita, Kazuki; Marufuji, Takato; Ishikawa, Takashi; Fujishima, Tadatsune; Nakano, Tomoyuki
JAEA-Technology 2023-016, 41 Pages, 2023/09
This report summarizes the results of the stabilization treatments of post-experiment nuclear materials in Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) from August 2018 to March 2021. Based on the management standards for nuclear materials enacted after the contamination accident that occurred at PFRF on June 6, 2017, the post-experiment nuclear materials containing plutonium (Pu): samples mixed with organic substances that cause an increase in internal pressure due to radiolysis (including X-ray diffraction samples mixed with epoxy resin and plutonium powder which caused contamination accidents), carbides and nitrides samples which is reactive in air, and chloride samples which may cause corrosion of storage containers, were selected as targets of the stabilization. The samples containing organic materials, carbides and nitrides were heated in an air flow at 650  C and 950
C and 950  C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500
C for 2 hours respectively to remove organic materials and convert uranium (U) and Pu into oxides. U and Pu chlorides in LiCl-KCl eutectic melt were reduced and extracted into liquid Cd metal by a reaction with lithium (Li) -cadmium (Cd) alloy and converted to U-Pu-Cd alloy at 500  C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
C or higher. All of the samples were stabilized and stored at PFRF. We hope that the contents of this report will be utilized to consider methods for stabilizing post experiment nuclear materials at other nuclear fuel material usage facilities.
Onuki, Toshihiko*; Ye, J.*; Kato, Tomoaki; Liu, J.; Takano, Masahide; Kozai, Naofumi; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
Environmental Science; Processes & Impacts, 25(7), p.1204 - 1212, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Analytical)To elucidate chemical forms of Cs and I in microparticles produced via the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident and released into the atmosphere, we analyzed Cs and I in condensed vaporized particles (CVP) produced by melting experiments using nuclear fuel components containing CsI with concrete. CVPs consisted of many round particles containing Cs and I of diameters less than several tens of micrometers. Two kinds of particles were present: one containing large amounts of Cs and I, suggesting the presence of CsI, and the other containing small amounts of Cs and I with large Si contents. Most of CsI from both particles were dissolved in water. On the contrary, some fractions of Cs remained from the latter particles. These results suggest that Cs was incorporated in CVPs along with Si to form water low-soluble CVPs
 and Zr at precisely controlled high temperatures
and Zr at precisely controlled high temperaturesShirasu, Noriko; Sato, Takumi; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.697 - 714, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Interaction tests between UO and Zr were performed at precisely controlled high temperatures between 1840 and 2000
and Zr were performed at precisely controlled high temperatures between 1840 and 2000  C to understand the interaction mechanism in detail. A Zr rod was inserted in a UO
C to understand the interaction mechanism in detail. A Zr rod was inserted in a UO crucible and then heat-treated at a fixed temperature in Ar-gas flow for 10 min. After heating in the range of 1890 to 1930
crucible and then heat-treated at a fixed temperature in Ar-gas flow for 10 min. After heating in the range of 1890 to 1930  C, the Zr rod was deformed to a round shape, in which the post-analysis detected the significant diffusion of U into the Zr region and the formation of a dominant
C, the Zr rod was deformed to a round shape, in which the post-analysis detected the significant diffusion of U into the Zr region and the formation of a dominant  -Zr(O) matrix and a small amount of U-Zr-O precipitates. The abrupt progress of liquefaction was observed in the sample heated at around 1940
-Zr(O) matrix and a small amount of U-Zr-O precipitates. The abrupt progress of liquefaction was observed in the sample heated at around 1940  C or higher. The higher oxygen concentration in the
C or higher. The higher oxygen concentration in the  -Zr(O) matrix suppressed the liquefaction progress, due to the variation in the equilibrium state. The U-Zr-O melt formation progressed by the selective dissolution of Zr from the matrix, and the selective diffusion of U could occur via the U-Zr-O melt.
-Zr(O) matrix suppressed the liquefaction progress, due to the variation in the equilibrium state. The U-Zr-O melt formation progressed by the selective dissolution of Zr from the matrix, and the selective diffusion of U could occur via the U-Zr-O melt.
 C
CLuu, V. N.; Nakajima, Kunihisa
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
Ouchi, Kazuki; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
RSC Advances (Internet), 13(24), p.16321 - 16326, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We clarified the chemical state transformation of deposits following the reduction of uranyl ion (U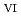 O
O
 ) from the results of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance, impedance spectra and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. We propose the following deposition mechanism: (1) U
) from the results of electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance, impedance spectra and X-ray absorption fine structure measurements. We propose the following deposition mechanism: (1) U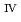 is formed by the disproportionation of U
is formed by the disproportionation of U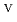 . (2) U
. (2) U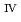 forms U
forms U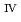 hydroxide deposits, and (3) finally, the hydroxide deposits transform into U
hydroxide deposits, and (3) finally, the hydroxide deposits transform into U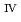 oxide, generally having a larger electrical resistance than the former.
oxide, generally having a larger electrical resistance than the former.
Mohamad, A. B.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.215 - 222, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Luu, V. N.; Nakajima, Kunihisa
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(2), p.153 - 164, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.52(Nuclear Science & Technology) (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd using cadmium chloride
using cadmium chlorideHayashi, Hirokazu; Shibata, Hiroki; Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(2), p.503 - 510, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)The formation of MPd (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu -type GdPd
-type GdPd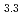 (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) and NpPd
0.0001 nm) and NpPd (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi
0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi -type NpPd
-type NpPd . Chlorination of the MPd
. Chlorination of the MPd (M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl
(M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl formation.
formation.
Miwa, Shuhei; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kino, Chiaki*; Suzuki, Eriko; Imoto, Jumpei
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-022, 32 Pages, 2023/01
The improved model for cesium (Cs) chemisorption onto stainless steel (SS) in the fission product (FP) chemistry database named ECUME was incorporated into the severe accident (SA) analysis code SAMPSON for the more accurate estimation of Cs distribution within nuclear reactor vessels in the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F). The SAMPSON with the improved model was verified based on the analysis results reproducing the experimental results which were subjected to the modeling of Cs chemisorption behavior. Then, the experiment in the facility with the temperature gradient tube to simulate SA conditions such as temperature decrease and aerosol formation was analyzed to confirm availability of the improved model to the analysis of Cs chemisorption onto SS. The SAMPSON with the improved model successfully reproduced the experimental results, which indicates that the improved model and the analytical method such as setting a method of node-junction, models of aerosol formation and the calculation method of saturated CsOH vapor pressure can be applicable to the analysis of Cs chemisorption behavior. As the information on water-solubility of Cs deposits was also prerequisite to estimate the Cs distribution in the 1F because Cs can be transported through aqueous phase after the SA, the water-solubility of chemisorbed Cs compounds was investigated. The chemisorbed compounds on SS304 have been identified to CsFeO at 873 K to 973 K with higher water-solubility, CsFeSiO
at 873 K to 973 K with higher water-solubility, CsFeSiO at 973 K to 1273 K and Cs
at 973 K to 1273 K and Cs Si
Si O
O at 1073 K to 1273 K with lower water-solubility. From these results, the water-solubility of chemisorbed Cs compounds can be estimated according to the SA analysis conditions such as temperature in the reactor and the CsOH concentration affecting the amount of chemisorbed Cs.
at 1073 K to 1273 K with lower water-solubility. From these results, the water-solubility of chemisorbed Cs compounds can be estimated according to the SA analysis conditions such as temperature in the reactor and the CsOH concentration affecting the amount of chemisorbed Cs.
Li, N.*; Sun, Y.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kurosaki, Ken*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 11 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)During the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant (1F) accident, an overwhelming amount of the cesium remaining in the pressure vessel could have been deposited onto 304 stainless steel (SS304) steam separators and dryers, both with large surface areas. During 1F's decommissioning, the deposited cesium is a safety hazard as it can generate radioactive dust. However, the cohesive and adhesive strengths of CsOH-chemisorbed oxide scales are yet to be defined. In this study, we investigated how CsOH-chemisorption affects the cohesive and adhesive strengths between oxide scales and SS304 substrates with a scratch tester. The scratch test results revealed that the cohesive strengths of the oxide scales decreased after CsOH-chemisorption, while adhesive failure could not be reached.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takano, Masahide; Nakamura, Satoshi; Onozawa, Atsushi; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Kirishima, Akira*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-021, 224 Pages, 2022/10
A set of technology, including acid dissolving, has to be established for the analysis of content of elements/nuclides in the fuel debris samples. In this project, a blind test was performed for the purpose of clarifying the current level of analytical accuracy and establishing the alternative methods in case that the insoluble residue remains. Overall composition of the simulated fuel debris (homogenized powder having a specific composition) were quantitatively determined in the four analytical institutions in Japan by using their own dissolving and analytical techniques. The merit and drawback for each technique were then evaluated, based on which a tentative flow of the analyses of fuel debris was constructed.
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
ACS Omega (Internet), 7(33), p.29326 - 29336, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Liu, J.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Shirasu, Noriko; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(4), p.484 - 490, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Komuro, Michiyasu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Kokusen, Junya; Shimizu, Osamu; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Inagawa, Jun
JAEA-Technology 2021-042, 197 Pages, 2022/03
Plutonium Research Building No.1 was constructed in 1960 for the purpose of establishing plutonium handling technology and studying its basic physical properties. Radiochemical research, physicochemical research and analytical chemistry regarding solutions and solid plutonium compounds had been doing for the research program in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In 1964, the laboratory building was expanded and started the researching plutonium-uranium mixed fuel and reprocessing of plutonium-based fuel, playing an advanced role in plutonium-related research in Japan. Since then, the research target has been expanded to include transplutonium elements, and it has functioned as a basic research facility for actinides. The laboratory is constructed by concrete structure and it has the second floor, equipped with 15 glove boxes and 4 chemical hoods. Plutonium Research Building No.1 was decided as one of the facilities to be decommissioned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform Plan in September 2014. So far, the contamination survey of the radioactive materials in the controlled area, the decontamination of glove boxes, and the consideration of the equipment dismantling procedure have been performed as planned. The radioisotope and nuclear fuel materials used in the facility have been transfer to the other facilities in JAEA. The decommissioning of the facility is proceeding with the goal of completing by decommissioning the radiation controlled area in 2026. In this report, the details of the decommissioning plan and the past achievements are reported with the several data.
Iwasa, Toma; Arima, Tatsumi*
JAEA-Technology 2021-036, 23 Pages, 2022/03
Knowledge on the liquefaction (thermal decomposition and melting) temperatures of MA-bearing nitride fuels for transmutation by accelerator-driven system is essential for elucidation of the fuel behaviors under abnormal condition and for the safety analysis. A melting temperature measurement system for refractory materials was developed based on a laser spot heating method, which is expected to measure in a very short time with a small amount of sample, and demonstration tests using refractory metals and zirconium nitride were performed. As the results, it was found that this melting temperature measurement system can be applicable up to the temperatures around 3000 K which is close to the thermal decomposition temperature of nitride fuels and we confirmed the technical feasibility of this system for future application to small specimens of transuranium nitrides.
Suzuki, Chikashi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.345 - 356, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)During a severe accident (SA) such as the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, fission products (FP) can be retained on the surface of structural materials in reactors. Cesium (Cs) is an important FP, and various Cs compounds such as Cs silicates are formed on the surface of stainless steel (SS) in a reactor during a SA. We calculated total energies of Cs-Si-O compounds for evaluation on phase stability within an adiabatic approximation. The calculations indicate that Cs Si
Si O
O is the most stable of the Cs-Si-O compounds. We calculated, furthermore, total energies of Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds. These calculations indicate that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds are more stable than C-Si-O compounds and that CsSi
is the most stable of the Cs-Si-O compounds. We calculated, furthermore, total energies of Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds. These calculations indicate that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds are more stable than C-Si-O compounds and that CsSi FeO
FeO is the most stable of these C-Si-O and Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds within an adiabatic approximation. The results of our present calculations and our previous experiments lead to the conclusion that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds can be stably formed on SS surface by Cs chemisorption.
is the most stable of these C-Si-O and Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds within an adiabatic approximation. The results of our present calculations and our previous experiments lead to the conclusion that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds can be stably formed on SS surface by Cs chemisorption.
Pshenichnikov, A.; Shibata, Hiroki; Yamashita, Takuya; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.267 - 291, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Osaka, Masahiko; Gou llo, M.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa
llo, M.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.292 - 305, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research on the fission product chemistry made after the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station were reviewed with focus on the Cesium chemistry in terms of two regimes, namely the accidental source term and the long-term source term via aqueous phase towards the decommissioning. For the accidental source term, Cs chemical interaction with Mo, B and Si were reviewed. Regarding the unique issue of long-term source term via aqueous phase, Cs penetration into concrete and fuel debris leaching were mentioned as the main sources of FPs. Efforts on the preparation of thermodynamic data for the Cs complex oxides were described. All these Cs chemical behaviors should be modelled and validated/verified through the analysis and evaluation of the actual samples including fuel debris that would be taken from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in near future.